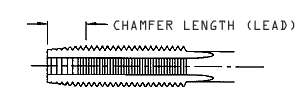Tap Manufacturers offer their own unique geometries for specific materials and applications. This chart is meant to provide general information. For a specific tap recommendation for your application, please consult your tap supplier.
Standard Straight Fluted Tap
With 6 to 8 Threads Chamfer Length or Lead.
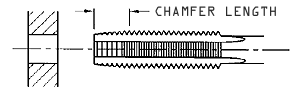
These taps do not transport the chips out of the hole. For this reason, they should not be used for deep hole tapping. They work best in shallow depth through holes and in materials that produce short chips.
|
Workpiece
Materials |
Recommended Tap Surface Treatments |
|
| Cast Iron |
Nitrided or TiN |
| Brass, Short Chipping |
Nitrided |
| Cast Aluminum |
Nitrided |
| Short Chip Hard |
Nitrided or TiN |
|
Straight Fluted Taps With Spiral Point
With 3.5 to 5 Threads Chamfer Length or Lead.
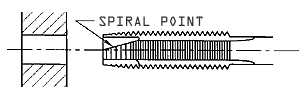
These taps push the chips forward. The chips are curled up to prevent logging in the flutes. They are used for through holes. |
Workpiece
Materials |
Recommended Tap Surface Treatments |
|
| Aluminum Long Chip |
Bright, or Cr or TiN |
| Exotic Alloys |
Nitrided or TiN |
| Stainless Steel |
Nitrided or TiN |
| Steel |
Bright or TiN or TiCN |
|
Left Hand Spiral Fluted Tap
With Approximately 12 Degrees
Spiral Flutes With 3.5 to 5 Threads Chamfer Length.
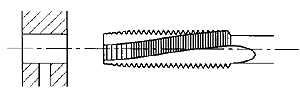
These taps are mostly used in thin walled parts or for holes interrupted by cross holes or longitudinal slots. |
Workpiece
Materials |
Recommended Tap Surface Treatments |
|
| Aluminum Long Chip |
Bright, or Cr or TiN |
| Exotic Alloys |
Nitrided or TiN |
| Stainless Steel |
Nitrided or TiN |
| Steel |
Bright or TiN or TiCN |
|
Right Hand Spiral Fluted Tap
With Approximately 15 Degrees
Spiral Flutes With 3.5 to 5 Threads Chamfer Length.
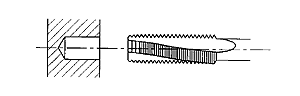
The spiral flutes transport chips back out of the hole. These taps are used in blind holes less than 1.5 times the tap diameter deep with materials that produce short chips. |
Workpiece
Materials |
Recommended Tap Surface Treatments |
|
| Cast Aluminum |
Nitrided |
| Titanium |
Nitrided or TiN |
| Stainless Steel |
Bright or TiN |
| Steel |
Bright or TiN or TiCN |
|
Right Hand Spiral Fluted Tap
With 40 Degrees to 50 Degrees Spiral Flutes.
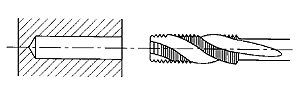
The greater helix angle provides good transport of chips back out o the hole. These taps are used only in blind holes in materials that produce long chips. They can also be used in deeper holes up to 3 times the tap diameter. |
Workpiece
Materials |
Recommended Tap Surface Treatments |
|
| Aluminum Long Chip |
Bright, or Cr or TiN |
| Stainless Steel |
Bright or TiN |
| Steel Alloy Cr-Ni |
Bright or TiN or TiCN |
| Soft Material |
Bright |
|
 |
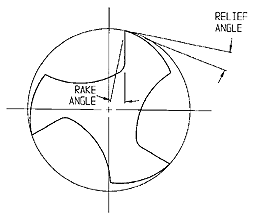 Rake Angle Rake Angle
The best rake angle for a tap depends on the material. Materials that produce long chips normally require a tap with greater rake angle. Materials that produce short chips require a smaller rake angle. Difficult materials like Titanium or Inconnell require a compromise between greater rake angle for longer chips and smaller rake angle for more strength. |
 |
Relief Angle In The Lead Of A Tap
A small relief angle can be used in soft materials. Harder materials like stainless steel can be cut easier with a tap having a greater relief angle which reduces the friction. Tough materials like Inconnel and nickel can be cut more easily with an even greater angle.
The relief angle is smaller on taps for blind holes that on taps for through holes so that the chip root can be sheared off when the tap reverses without breaking the taps cutting edge.
|
|
Chamfer Length (Lead)
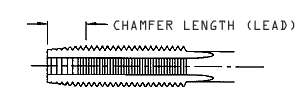
The actual cutting of the thread is done by the lead of the tap. When there are more threads in the chamfer length or lead the torque is reduced, producing the thread is much easier, and the life of the tap will be increased. In blind holes where there is not enough room to drill deep enough for a tap with a longer lead, taps with short leads are used. In some cases the lead of the tap is reduced to as little as 1.5 threads. This greatly increases torque and reduces tap life. Even when using taps with shortened lead it is still important to drill deep enough for adequate clearance. It is recommended to allow one thread length plus one mm beyond the lead of the tap as drill clearance.
Relief Angle In The Thread Profile (Pitch Diameter Relief)
The relief angle effects true to gage thread cutting, and also the free cutting ability and life of the tap. It has an effect on how the tap is guided when it enters the hole. If the relief angle is too great pitch guidance and self centering of the tap can not be guaranteed especially in soft materials. In materials like stainless steel or bronze the relief angle should be larger to allow free cutting and to allow more lubrication to reach the cutting and friction surfaces. A bigger relief angle can allow higher tapping speed provided the tap is guided concentrically into the hole by the machine and tap holder. |
Roll Form Taps
 |
Workpiece
Materials |
Recommended Tap Surface Treatments |
|
| All Ductile Materials |
|
These taps form the thread rather than cut. Since no chips are produced they can be used in blind or through holes. Cold forming is possible in all ductile materials. Advantages include no waste in the form of chips, no mis-cutting of threads, no pitch deviation, higher strength, longer tool life, and higher speed. Please note that the core hole diameter must be larger than with a cutting tap. Good lubrication is important , more torque is required, and the minor diameter of the thread will appear rough due to forming process.
 Rake Angle
Rake Angle